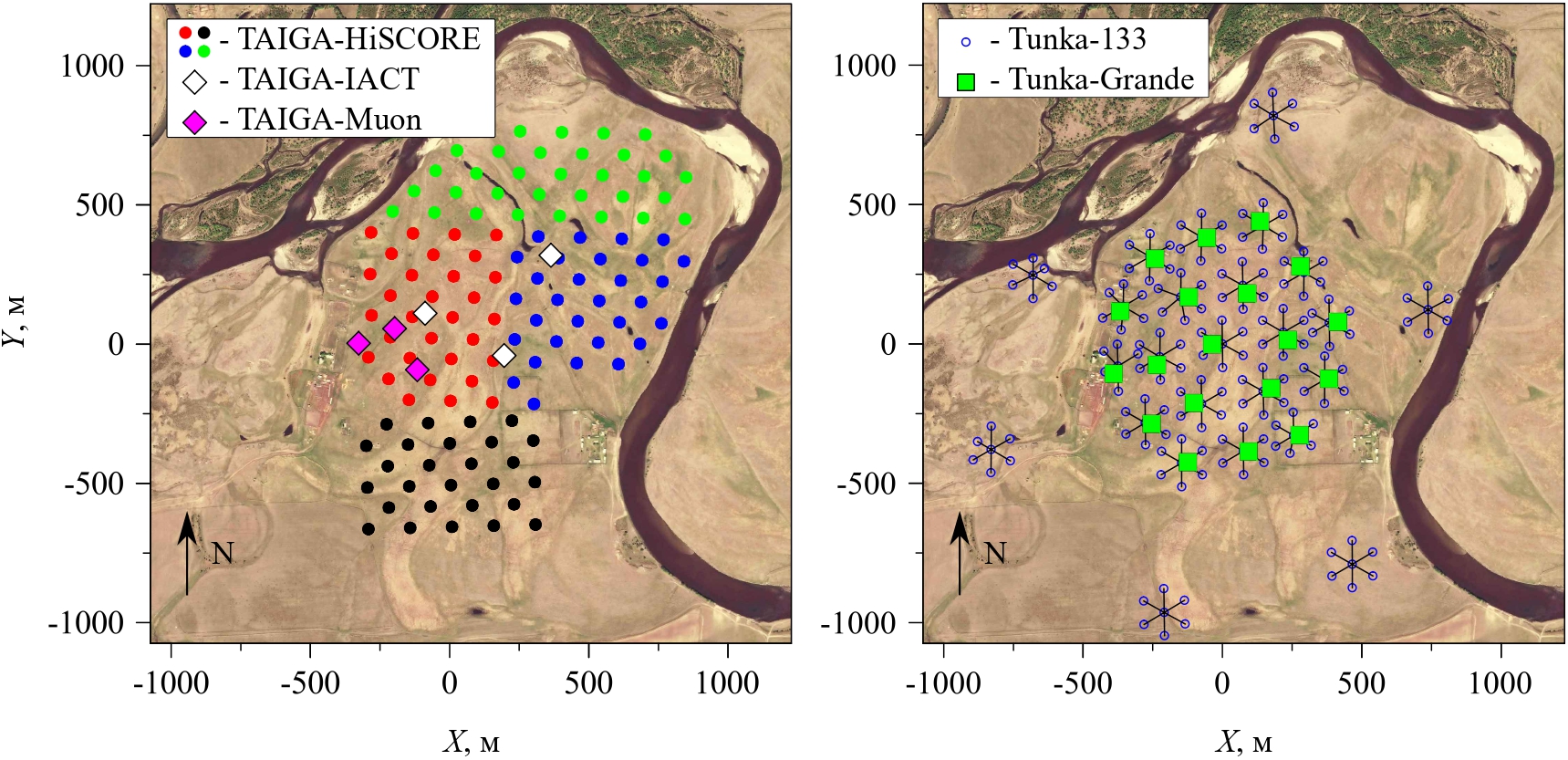
TAIGA is a complex hybrid detector system consisting of the following components:
- TAIGA-HiSCORE. An array of wide Field of View (FoV; ~0.6 sr) air Cherenkov detector stations spaced 150-200 m apart. The stations are grouped into 4 clusters and cover an area of approximately 1 km².
-
Tunka-133. An array of wide FoV air Cherenkov detectors. The full-size detector has been operational since 2009 and originally comprised 133 detectors distributed over an area of approximately 3 km². Since 2012, the number of stations has increased to 175. Each station features a single large PMT (20 cm in diameter).
-
TAIGA-IACT. An array of 3 working Imaging Air Cherenkov Telescopes (IACTs), each with a reflector area of 10 m² and equipped with imaging cameras containing approximately 600 PMT-based pixels. Each pixel has an aperture of 0.36°, and the FoV of a single telescope is 10°. The distances between telescopes are optimized to range from 300 to 500 m. By 2025, a total of five telescopes will be operational.
-
TAIGA-Muon and Tunka-Grande. The Tunka-Grande array consists of 19 stations equipped with the surface and underground counters for measuring the muon and electron-photon components of extensive air showers (EAS). The TAIGA-Muon includes 3 stations, each with 8 surface scintillation counters for detecting all charged particles of EAS and 8 underground ones for measuring muon components.